SPEC Kit 322: Library User Experience · 55
User Experience Activity 2
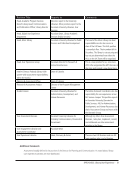
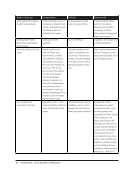
18. What broad aspect of the user’s library experience was the activity trying to assess and/or design?
Check all that apply. N=51
Library technology (website usability, navigation) 32 63%
Library facilities (space configuration, navigation) 23 45%
Library services (ILL, reference, instruction, etc.) 20 39%
Library resources (search and discovery, collections, formats) 20 39%
Other aspect 6 12%
Please describe other aspect.
Context, Staff, Equipment.
Gather data on the users of the Info Commons in Langsam Library.
Marketing tool for reference services.
Regular meetings with student governance and advisory boards to assess needs and build support for student fee
increases.
The role of the libraries and readiness to partner in support of new forms of digital scholarship in the humanities.
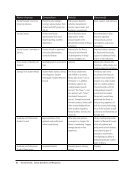
19. Please briefly describe the scope of the activity. N=50
A librarian and a member of the Center for Instructional Technology did an intensive study on the Cultural Anthropology
department. They employed methods used at the University of Minnesota to interview each individual faculty member.
They also held focus groups with graduate students. The goal of the study was to better understand the research
process for these more intensive scholars, as well as to form a strong working relationship between the library and this
department.
A task force was formed as a partnership between KU Libraries, the College of Liberal Arts and Sciences, and the Hall
Center for Humanities (a research center). Through an 18-month series of meetings, focus groups, survey, and site visits
we assessed readiness to develop a more formalized support system for digital humanities research.
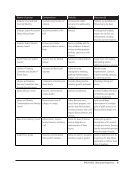
Appreciative Inquiry (AI) is an established organizational development theory based on the belief that organizations
change in the way they inquire (Cooperrider &Srivastava, 1987). In other words, you become what you study. As such,
appreciating what is exemplary in an organization will lean an organization to discover how to create more excellence.
The Business Library undertook this process starting with the engagement of two consultants who conducted focus
groups with participants, including faculty members, students, and staff. Through stories and exploring themes,
participants shared what was most successful about the library and how they envisioned this success could be extended
into the future. These focus groups not only provided useful data, but were also a great way to publicly discuss the
successes of the library and to engage stakeholders in positive conversation.
User Experience Activity 2
18. What broad aspect of the user’s library experience was the activity trying to assess and/or design?
Check all that apply. N=51
Library technology (website usability, navigation) 32 63%
Library facilities (space configuration, navigation) 23 45%
Library services (ILL, reference, instruction, etc.) 20 39%
Library resources (search and discovery, collections, formats) 20 39%
Other aspect 6 12%
Please describe other aspect.
Context, Staff, Equipment.
Gather data on the users of the Info Commons in Langsam Library.
Marketing tool for reference services.
Regular meetings with student governance and advisory boards to assess needs and build support for student fee
increases.
The role of the libraries and readiness to partner in support of new forms of digital scholarship in the humanities.
19. Please briefly describe the scope of the activity. N=50
A librarian and a member of the Center for Instructional Technology did an intensive study on the Cultural Anthropology
department. They employed methods used at the University of Minnesota to interview each individual faculty member.
They also held focus groups with graduate students. The goal of the study was to better understand the research
process for these more intensive scholars, as well as to form a strong working relationship between the library and this
department.
A task force was formed as a partnership between KU Libraries, the College of Liberal Arts and Sciences, and the Hall
Center for Humanities (a research center). Through an 18-month series of meetings, focus groups, survey, and site visits
we assessed readiness to develop a more formalized support system for digital humanities research.
Appreciative Inquiry (AI) is an established organizational development theory based on the belief that organizations
change in the way they inquire (Cooperrider &Srivastava, 1987). In other words, you become what you study. As such,
appreciating what is exemplary in an organization will lean an organization to discover how to create more excellence.
The Business Library undertook this process starting with the engagement of two consultants who conducted focus
groups with participants, including faculty members, students, and staff. Through stories and exploring themes,
participants shared what was most successful about the library and how they envisioned this success could be extended
into the future. These focus groups not only provided useful data, but were also a great way to publicly discuss the
successes of the library and to engage stakeholders in positive conversation.