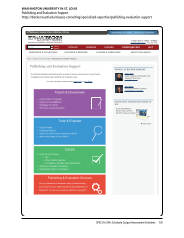
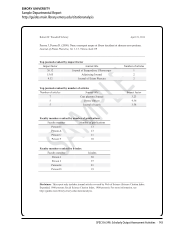
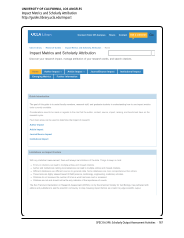
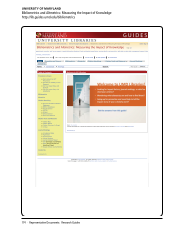
SPEC Kit 346: Scholarly Output Assessment Activities · 73
UNIVERSITY OF IOWA
How to Determine Your Scholarly Impact
http://www.lib.uiowa.edu/hardin
319-335-9151
aeb 12-9-14
• Impact Factor: A quantitative measure of the frequency with which the "average article" published in a
given scholarly journal has been cited in a particular year or period; this is used in citation analysis
(definition retrieved from http://www.library.tudelft.nl/tulib/glossary/index.htm#I)
•
Citations in 2013 to articles published in X in 2011 and 2012
Impact Factor for Journal X =
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Articles published in X in 2011 and 2012
• Eigenfactor: The Eigenfactor is another way to rank journals based on their influence in the field. It
tries to get around some of the issues that make impact factors controversial. To find out more, see
“Why Eigenfactor?” at http://www.eigenfactor.org/whyeigenfactor.htm
• H-Index: This number is based on a formula that calculates the average number of citing articles for all
items in a [pre]defined set. It can be used to measure the productivity and impact of the published works
of a particular researcher or even a group of researchers. The h-index was developed by Jorge E. Hirsch
and published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 102
(46): 16569-16572 November 15 2005. It is sometimes referred to as the Hirsch Index.
• Altmetrics: This is the measurement of the impact an article has on social media such as Twitter,
Facebook, etc. For more information, see http://blog.lib.uiowa.edu/needtoknow/2013/08/08/interesting-
articles-on-altmetrics/
Managing References
Citation Management Tools-‐ EndNote and RefWorks
EndNote desktop RefWorks EndNote Basic
Best use Those with complex, ongoing
research projects and planning
on career of publication who
are primarily using the same
workstation for research and
writing.
RefWorks will no longer be available
after December 2014. Less complex
projects. Ideal for those who are
going to be using multiple computers
for research.
Less complex projects. Ideal for
those who are going to be using
multiple computers for research.
Location of files Locally on your computer On RefWorks site (server) On EndNote site (server)
Getting
citations in…
Automatic export from many
databases. 2 step process if
not available.
Automatic export from many
databases. 2 step process if not
available.
Automatic export from many
databases. 2 step process if not
available.
# of styles Over 4500 Over 2700 Over 2000
Sharing Because library lives on your
computer, sharing is through
sharing of computer or
compressing files. Colleagues
will need EndNote installed to
view
RefShare feature allows you to share
folders or your entire library with
anyone with an internet connection
(though pdfs cannot be shared in this
way).
Allows you to share folders or
your entire library with anyone
with an internet connection, and
allows you to grant people
editing rights to your citations.
Overall
strengths
Great for very large amounts
of citations. Also has a feature
that can pull some PDF’s and
automatically attach them to
citations.
Very easy to learn, use anywhere with
an internet connection. Easy to share
citations with others.
Very easy to learn, use anywhere
with an internet connection. Easy
to share citations with others and
to allow others full access to
citations.
More information on citing sources: http://guides.lib.uiowa.edu/citingsources