182 · Representative Documents: Research Guides
SYRACUSE UNIVERSITY
Citation Metrics
http://researchguides.library.syr.edu/citationmetrics
Admin Sign In
Home Scopus Web of Science Google Journal Metrics Altmetrics Additional Resources SU Recent Publications
About | Hours | Find Resources | Services | Research Assistance | Visiting | Help
Faculty Resources | Graduate Resources | Undergraduate Resources | Your Accounts
Copyright | Privacy Policy [PDF] | SUmail | MySlice | Blackboard | SU Home
Accessibility | Plugins & File Viewers
Library » Subject Guides » Citation Metrics
Citation Metrics
URL: http://researchguides.library.syr.edu/citationmetrics Print Guide RSS Updates
Powered by Springshare; All rights reserved. Report a tech support issue.
View this page in a format suitable for printers and screen-readers or mobile devices.
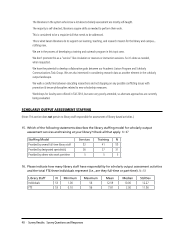
Citation Metrics
Citation analysis is a quantifiable measure of academic output and may help inform decisions on promotion and
tenure. This guide is designed to help faculty members and librarians use and understand the tools available to
us. We are fortunate to have access to the top paid resources used for citation metrics – Web of Science,
Scopus and Journal Citation Reports.
We need to be aware of the limitations and incongruities of citation metrics. The databases referenced above,
and including Google Scholar, do not correct errors in citing papers. This means that one paper may be cited many different ways
and appear as separate entries in these tools. Also, author and institutional naming inconsistencies complicate these analyses.
Comparisons between these tools should be avoided. The databases use different sources to generate data and some are more
comprehensive than others. In addition, the literature suggests that these tools are skewed towards the STM (science, technical
and medical) community of scholars.
The recommended methods for citation analyses are detailed this guide. Another useful metric is the h-index which can be
generated in both Web of Science and Scopus. The h-index is defined as:
A scientist has index h if h of [his/her] Np papers have at least h citations each, and the other (Np − h) papers have at
most h citations each.
Information for Authors
ORCID - Open Researcher ID - is an initiative to
provide researchers and scholars with a
persistent, unique identifier. This will enable
individuals to get recognized for all their
scholarly output, in both established and
emerging media. With broad-based support from
publishers, academic institutions, and funders,
ORCID registration and services are free to
individuals. Sign up here: http://about.orcid.org/.
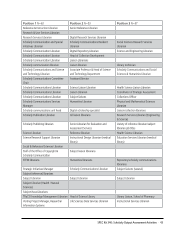
Comparison across Databases
Useful data can be found in each tool but direct comparisions
across databases are problematic. These resources use
different pools of data, date ranges and may interpret
citations differently. Correct attribution of authorship can also
cause reporting errors. Take control of your scholarly output -
check your author profiles and register for an ORCID ID.
This chart illustrates reporting differences. Exercising as
much consistency as possible, the same author was profiled
(11/2012) in each resource. The varied results are displayed
above.
Librarian
Linda Galloway
Contact Info
Syracuse University
Carnegie Library
Room 104
315-443-9766
Send Email
Links:
Website / Blog
Profile & Guides
Subjects:
Biology, Chemistry, Forensic
Science, Citation Metrics
Your Librarian
Anne Rauh
Contact Info
Carnegie Library
315-443-9770
Send Email
Links:
Website / Blog
Profile & Guides
Subjects:
Engineering, Computer Science