6 Survey Results: Executive Summary
Online Resource License Restrictions
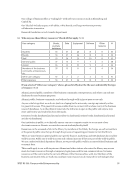
The majority of the responding libraries (42 or 75%) did not need to revise their license agreements
or clarify limitations of use for online resources due to expanded entrepreneurial initiatives. Of the 14
that did, most identified the resource that had to have its license revised or usage clarified generally as
“business databases” or they named a specific database such as “Bloomberg.”
The most common resource restrictions imposed on libraries are restricted access by IP range
(26 responses or 74%), followed by restricted to non-commercial uses (23 or 66%) and in-library use only
(18 or 51%).
Of the six responding institutions who provided additional details on licensing agreements
unique to entrepreneurship resources, three mentioned that their license agreements include a “walk-in”
clause to allow for expanded access to unaffiliated institutional users.
Non-Library Resources for Entrepreneurship
A large minority of responding libraries (28 or 48%) did not know whether their institution’s non-
library units purchased or licensed resources to support campus entrepreneurship activities. However,
27 respondents (47%) reported that their non-library units did purchase or license resources to support
entrepreneurial activities on campus. The resource type most cited was that of business databases
and datasets.
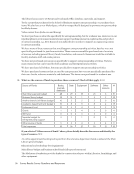
Library Services for Entrepreneurship
The overwhelming majority of responding institutions identified the top three services provided by the
library to specifically support entrepreneurship activities as reference, which may include consultation
appointments and office hours (52 or 96%) library instruction such as “a series of free workshops
covering topics such as copyright and intellectual property…” (96%), and in-depth research, for instance
conducting database searches in preparation for an appointment (39 or 72%). Notable examples of these
entrepreneurship library services are found in the representative documents section of this SPEC Kit.
Providing market research assistance and offering support for business plan competitions are additional
services delivered by a majority of responding libraries. A minority are offering patent searching (22 or
41%) and other services (41%), which vary from 3D printing to LibGuides on entrepreneurship.
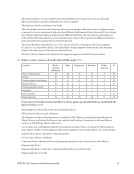
The results for location of library services fit the pattern observed in location for library
resources. The main campus library is the primary location used to offer entrepreneurship services. This
is followed by online. Of the responding institutions whose services are offered at another branch/unit
library (26 or 48%), engineering, medical/health sciences and science libraries, also known as STEM
libraries, were most commonly reported. The business library followed closely in fourth place. For those
responding “other location,” business schools were most frequently cited. The specific kinds of services
most often offered at the main campus library, another branch/unit library, and the business library are
reference, instruction, and research, respectively. This order slightly changes to reference, research, and
instruction when offered online.
The core users of library resources are the same for library services: students, faculty, and staff.
Alumni, the general public, and members of the business community are the second tier of users of library
services. A few respondents mentioned that anyone could use library services. A further breakdown
reveals that user demographics for reference services is split evenly among the three core user groups at
all the responding libraries. The same split is true for the main users of research services (46 libraries or
87%). There is a noted difference for users of instructional services with students at all libraries, faculty at
50 (94%) and staff at 46 (87%).
Online Resource License Restrictions
The majority of the responding libraries (42 or 75%) did not need to revise their license agreements
or clarify limitations of use for online resources due to expanded entrepreneurial initiatives. Of the 14
that did, most identified the resource that had to have its license revised or usage clarified generally as
“business databases” or they named a specific database such as “Bloomberg.”
The most common resource restrictions imposed on libraries are restricted access by IP range
(26 responses or 74%), followed by restricted to non-commercial uses (23 or 66%) and in-library use only
(18 or 51%).
Of the six responding institutions who provided additional details on licensing agreements
unique to entrepreneurship resources, three mentioned that their license agreements include a “walk-in”
clause to allow for expanded access to unaffiliated institutional users.
Non-Library Resources for Entrepreneurship
A large minority of responding libraries (28 or 48%) did not know whether their institution’s non-
library units purchased or licensed resources to support campus entrepreneurship activities. However,
27 respondents (47%) reported that their non-library units did purchase or license resources to support
entrepreneurial activities on campus. The resource type most cited was that of business databases
and datasets.
Library Services for Entrepreneurship
The overwhelming majority of responding institutions identified the top three services provided by the
library to specifically support entrepreneurship activities as reference, which may include consultation
appointments and office hours (52 or 96%) library instruction such as “a series of free workshops
covering topics such as copyright and intellectual property…” (96%), and in-depth research, for instance
conducting database searches in preparation for an appointment (39 or 72%). Notable examples of these
entrepreneurship library services are found in the representative documents section of this SPEC Kit.
Providing market research assistance and offering support for business plan competitions are additional
services delivered by a majority of responding libraries. A minority are offering patent searching (22 or
41%) and other services (41%), which vary from 3D printing to LibGuides on entrepreneurship.
The results for location of library services fit the pattern observed in location for library
resources. The main campus library is the primary location used to offer entrepreneurship services. This
is followed by online. Of the responding institutions whose services are offered at another branch/unit
library (26 or 48%), engineering, medical/health sciences and science libraries, also known as STEM
libraries, were most commonly reported. The business library followed closely in fourth place. For those
responding “other location,” business schools were most frequently cited. The specific kinds of services
most often offered at the main campus library, another branch/unit library, and the business library are
reference, instruction, and research, respectively. This order slightly changes to reference, research, and
instruction when offered online.
The core users of library resources are the same for library services: students, faculty, and staff.
Alumni, the general public, and members of the business community are the second tier of users of library
services. A few respondents mentioned that anyone could use library services. A further breakdown
reveals that user demographics for reference services is split evenly among the three core user groups at
all the responding libraries. The same split is true for the main users of research services (46 libraries or
87%). There is a noted difference for users of instructional services with students at all libraries, faculty at
50 (94%) and staff at 46 (87%).