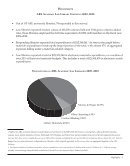
48 · ARL Academic Law Library Statistics 2009–2010
materials expenditures—i.e., if those expenditures are included in “Other Operating Expenditures”— report 0, not NA/UA, on line
(16d).
Question 17. Contract Binding. Include only contract expenditures for binding done outside the library. If all binding is done in-
house, state this fact and give in-house expenditures in a footnote do not include personnel expenditures.
Questions 18. Salaries and wages. Exclude fringe benefits. If professional, support staff and student salaries cannot be separated,
enter NA/UA, in lines (18a), (18b) and (18c) and enter total staff salaries in line (18).
Question 18c. Salaries and wages: Student Assistants. Report 100% of student wages regardless of budgetary source of funds.
Include federal and local funds for work study students.
Question 20. Other operating expenditures. Exclude expenditures for buildings, maintenance, and fringe benefits.
Questions 22-26. Electronic expenditures. These items are intended to indicate what portion of your institution’s total library
expenditures are dedicated to electronic resources and services. Please use the Footnotes to indicate any electronic materials
expenditures you believe not to be covered by these questions. Many expenditures recorded in these questions should have been
included in question (21), total library expenditures.
Question 22. One-time electronic resource purchases. Report expenditures that are not current serials (i.e. are non-subscription,
one-time, or monographic in nature) for software and machine-readable materials considered part of the collections. Examples
include periodical backfiles, literature collections, one-time costs for JSTOR membership, etc. Expenditures reported here may
be derived from any of the following categories: Monographs (16a), Other Library Materials (16c), Miscellaneous (16d), or Other
Operating Expenditures (20).
Question 23. Ongoing electronic resource purchases. Report subscription expenditures (or those which are expected to be
ongoing commitments) for serial publications whose primary format is electronic and for online searches of remote databases such
as OCLC FirstSearch, DIALOG, Lexis-Nexis, etc. Examples include paid subscriptions for electronic journals and indexes/abstracts
available via the Internet, CD-ROM serials, and annual access fees for resources purchased on a “one-time” basis, such as literature
collections, JSTOR membership, etc. Not all items whose expenditures are counted here will be included in Serial titles currently
received question (5) or Serials Expenditures question (16b).
Question 24. Bibliographic Utilities, Networks, and Consortia. Because it is increasingly common for ARL Libraries to
enter into consortial arrangements to purchase access to electronic resources, both “Library” and “External” expenditure blanks
and instructions are provided. Please use afootnote to describe expenditures that you believe are not covered by the question, or
situations that do not seem to fit the instructions.
Question 24a. From internal library sources. Report expenditures paid by the Library for services provided by national, regional,
and local bibliographic utilities, networks, and consortia, such as OCLC and RLG, unless for user database access and subscriptions,
which should be reported in questions (22) or (23). Include only expenditures that are part of Other Operating Expenditures (Q20).
Question 24b. From external sources. If your library receives access to computer files, electronic serials or search services through
one or more centrally-funded system or consortial arrangements for which it does not pay fully and/or directly (for example, funding
is provided by the state on behalf of all members), enter the amount paid by external bodies on its behalf. If the specific dollar
amount is not known, but the total student FTE for the consortium and amount spent for the academic members are known, divide
the overall amount spent by your institution’s share of the total student FTE.
materials expenditures—i.e., if those expenditures are included in “Other Operating Expenditures”— report 0, not NA/UA, on line
(16d).
Question 17. Contract Binding. Include only contract expenditures for binding done outside the library. If all binding is done in-
house, state this fact and give in-house expenditures in a footnote do not include personnel expenditures.
Questions 18. Salaries and wages. Exclude fringe benefits. If professional, support staff and student salaries cannot be separated,
enter NA/UA, in lines (18a), (18b) and (18c) and enter total staff salaries in line (18).
Question 18c. Salaries and wages: Student Assistants. Report 100% of student wages regardless of budgetary source of funds.
Include federal and local funds for work study students.
Question 20. Other operating expenditures. Exclude expenditures for buildings, maintenance, and fringe benefits.
Questions 22-26. Electronic expenditures. These items are intended to indicate what portion of your institution’s total library
expenditures are dedicated to electronic resources and services. Please use the Footnotes to indicate any electronic materials
expenditures you believe not to be covered by these questions. Many expenditures recorded in these questions should have been
included in question (21), total library expenditures.
Question 22. One-time electronic resource purchases. Report expenditures that are not current serials (i.e. are non-subscription,
one-time, or monographic in nature) for software and machine-readable materials considered part of the collections. Examples
include periodical backfiles, literature collections, one-time costs for JSTOR membership, etc. Expenditures reported here may
be derived from any of the following categories: Monographs (16a), Other Library Materials (16c), Miscellaneous (16d), or Other
Operating Expenditures (20).
Question 23. Ongoing electronic resource purchases. Report subscription expenditures (or those which are expected to be
ongoing commitments) for serial publications whose primary format is electronic and for online searches of remote databases such
as OCLC FirstSearch, DIALOG, Lexis-Nexis, etc. Examples include paid subscriptions for electronic journals and indexes/abstracts
available via the Internet, CD-ROM serials, and annual access fees for resources purchased on a “one-time” basis, such as literature
collections, JSTOR membership, etc. Not all items whose expenditures are counted here will be included in Serial titles currently
received question (5) or Serials Expenditures question (16b).
Question 24. Bibliographic Utilities, Networks, and Consortia. Because it is increasingly common for ARL Libraries to
enter into consortial arrangements to purchase access to electronic resources, both “Library” and “External” expenditure blanks
and instructions are provided. Please use afootnote to describe expenditures that you believe are not covered by the question, or
situations that do not seem to fit the instructions.
Question 24a. From internal library sources. Report expenditures paid by the Library for services provided by national, regional,
and local bibliographic utilities, networks, and consortia, such as OCLC and RLG, unless for user database access and subscriptions,
which should be reported in questions (22) or (23). Include only expenditures that are part of Other Operating Expenditures (Q20).
Question 24b. From external sources. If your library receives access to computer files, electronic serials or search services through
one or more centrally-funded system or consortial arrangements for which it does not pay fully and/or directly (for example, funding
is provided by the state on behalf of all members), enter the amount paid by external bodies on its behalf. If the specific dollar
amount is not known, but the total student FTE for the consortium and amount spent for the academic members are known, divide
the overall amount spent by your institution’s share of the total student FTE.