55 SPEC Kit 354: Data Curation
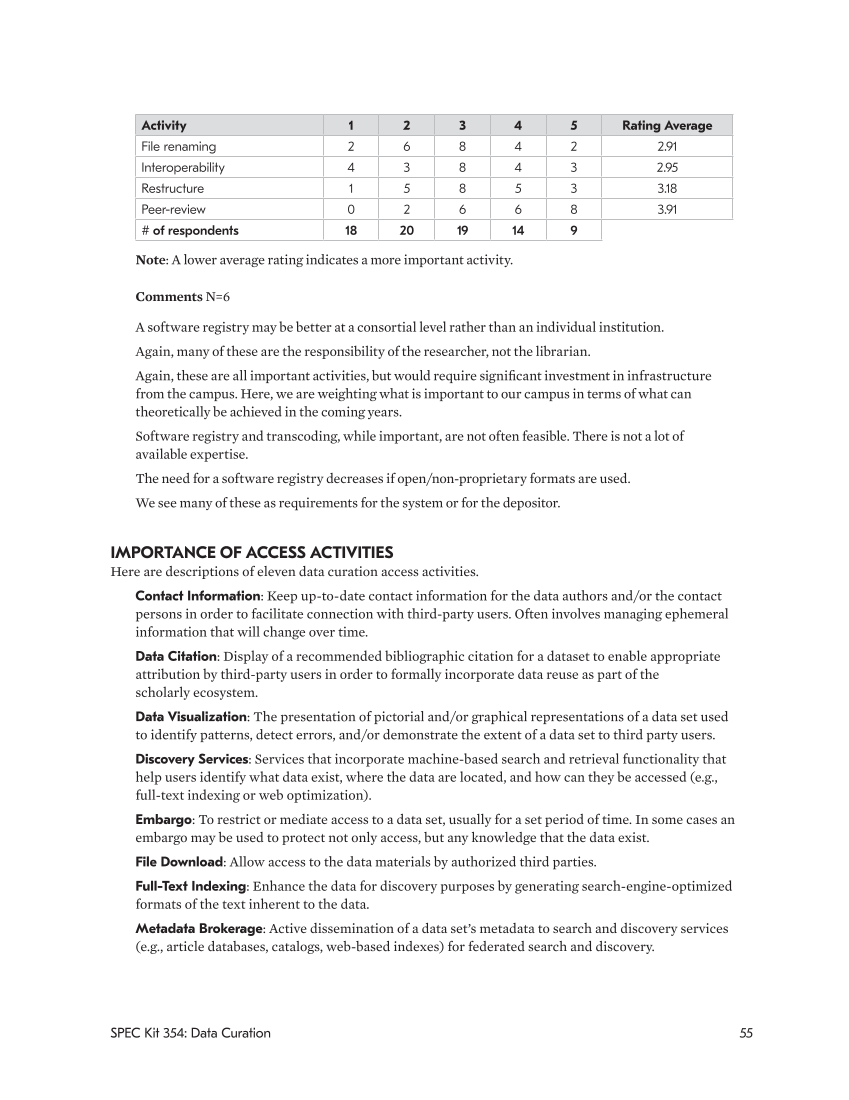
Activity 1 2 3 4 5 Rating Average
File renaming 2 6 8 4 2 2.91
Interoperability 4 3 8 4 3 2.95
Restructure 1 5 8 5 3 3.18
Peer-review 0 2 6 6 8 3.91
#of respondents 18 20 19 14 9
Note: A lower average rating indicates a more important activity.
Comments N=6
A software registry may be better at a consortial level rather than an individual institution.
Again, many of these are the responsibility of the researcher, not the librarian.
Again, these are all important activities, but would require significant investment in infrastructure
from the campus. Here, we are weighting what is important to our campus in terms of what can
theoretically be achieved in the coming years.
Software registry and transcoding, while important, are not often feasible. There is not a lot of
available expertise.
The need for a software registry decreases if open/non-proprietary formats are used.
We see many of these as requirements for the system or for the depositor.
IMPORTANCE OF ACCESS ACTIVITIES
Here are descriptions of eleven data curation access activities.
Contact Information: Keep up-to-date contact information for the data authors and/or the contact
persons in order to facilitate connection with third-party users. Often involves managing ephemeral
information that will change over time.
Data Citation: Display of a recommended bibliographic citation for a dataset to enable appropriate
attribution by third-party users in order to formally incorporate data reuse as part of the
scholarly ecosystem.
Data Visualization: The presentation of pictorial and/or graphical representations of a data set used
to identify patterns, detect errors, and/or demonstrate the extent of a data set to third party users.
Discovery Services: Services that incorporate machine-based search and retrieval functionality that
help users identify what data exist, where the data are located, and how can they be accessed (e.g.,
full-text indexing or web optimization).
Embargo: To restrict or mediate access to a data set, usually for a set period of time. In some cases an
embargo may be used to protect not only access, but any knowledge that the data exist.
File Download: Allow access to the data materials by authorized third parties.
Full-Text Indexing: Enhance the data for discovery purposes by generating search-engine-optimized
formats of the text inherent to the data.
Metadata Brokerage: Active dissemination of a data set’s metadata to search and discovery services
(e.g., article databases, catalogs, web-based indexes) for federated search and discovery.
Activity 1 2 3 4 5 Rating Average
File renaming 2 6 8 4 2 2.91
Interoperability 4 3 8 4 3 2.95
Restructure 1 5 8 5 3 3.18
Peer-review 0 2 6 6 8 3.91
#of respondents 18 20 19 14 9
Note: A lower average rating indicates a more important activity.
Comments N=6
A software registry may be better at a consortial level rather than an individual institution.
Again, many of these are the responsibility of the researcher, not the librarian.
Again, these are all important activities, but would require significant investment in infrastructure
from the campus. Here, we are weighting what is important to our campus in terms of what can
theoretically be achieved in the coming years.
Software registry and transcoding, while important, are not often feasible. There is not a lot of
available expertise.
The need for a software registry decreases if open/non-proprietary formats are used.
We see many of these as requirements for the system or for the depositor.
IMPORTANCE OF ACCESS ACTIVITIES
Here are descriptions of eleven data curation access activities.
Contact Information: Keep up-to-date contact information for the data authors and/or the contact
persons in order to facilitate connection with third-party users. Often involves managing ephemeral
information that will change over time.
Data Citation: Display of a recommended bibliographic citation for a dataset to enable appropriate
attribution by third-party users in order to formally incorporate data reuse as part of the
scholarly ecosystem.
Data Visualization: The presentation of pictorial and/or graphical representations of a data set used
to identify patterns, detect errors, and/or demonstrate the extent of a data set to third party users.
Discovery Services: Services that incorporate machine-based search and retrieval functionality that
help users identify what data exist, where the data are located, and how can they be accessed (e.g.,
full-text indexing or web optimization).
Embargo: To restrict or mediate access to a data set, usually for a set period of time. In some cases an
embargo may be used to protect not only access, but any knowledge that the data exist.
File Download: Allow access to the data materials by authorized third parties.
Full-Text Indexing: Enhance the data for discovery purposes by generating search-engine-optimized
formats of the text inherent to the data.
Metadata Brokerage: Active dissemination of a data set’s metadata to search and discovery services
(e.g., article databases, catalogs, web-based indexes) for federated search and discovery.